






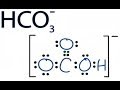









Answer and Explanation: When a proton is added to a carbonate ion, its conjugate base is formed. CO32−+H+⇌ HCO3− C O 3 2 − + H + ⇌ H C O 3 −. The conjugate base of carbonate ion is Create your account. View this answer. The conjugate base of HCO 3 - is CO 3 -2, which is the carbonate ion. To determine the conjugate base of a substance, you remove one hydrogen ion. Furthermore, what is the conjugate base of hco3 −? Bicarbonate: HCO3 - is known as hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate. It's a polyatomic ion that can bond to any positive ion. According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, bicarbonate is a conjugate acid. The conjugate base of HCO3 - is CO3 -2, which is the carbonate ion. Hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO 3 –, is derived from a diprotic acid and is amphiprotic. Its conjugate acid is H 2 CO 3 , and its conjugate base is CO 3 2– . The use of conjugate acid-base pairs allows us to make a very simple statement about relative strengths of acids and bases. The conjugate base of bicarbonate, HCO 3- is carbonate, CO3 2-.. HCO3- is a conjugate acid, H 2 CO 3 The carbonate ion carries a negative two formal charge and is the conjugate base of the hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO 3 −, which is the conjugate base of H 2 CO 3, carbonic acid. A carbonate salt forms when a positively charged ion attaches to the negatively charged oxygen atoms of the ion, forming an ionic compound . A conjugate acid is a substance that is formed when a base receives a proton, or H +. So, in order to determine the conjugate acid for a given base, all you have to know is that. base+H + → conjugate acid of that base. In your case, the base is hydrogen carbonate, or H CO− 3. If you write the equation you'll get. The conjugate base of HCO3- is CO32-. Conjugates always differ by one H+. A conjugate base has one fewer H+, while a conjugate acid has one more H+. Salts or ions of the theoretical carbonic acid, containing the radical CO2(3-). Carbonates are readily decomposed by acids. The carbonates of the alkali metals are water-soluble; all others are insoluble. The hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO3, has both a conjugate acid and a conjugate base. These are, respectively: CO;2-, H2CO3 Онҳо*, он OH,CO3, C0,2- HCO3, HCO3 $ HCO3, HCO3 Get more help from Chegg
[index] [9728] [7193] [6245] [7806] [9041] [3481] [4262] [683] [7246] [4774]
This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the pH of weak acids and bases such as HC2H3O2 and NH3 given Ka (acid dissociation constant) and Kb (... 0:25this ion hydrogen atom has one valence ... Identify Conjugate Acid Base Pairs (Bronsted Lowry) - Duration: 6:04. chemistNATE 533,762 views. 6:04. Calculating CO32- Formal Charges: Calculating ... In the following equations water is acting as a proton acceptor. If the hydrogen carbonate ion is a common amphiprotic ion. In the presence of a strong base it can behave as a proton donor. In the ... In this video we'll balance the equation HCl + Ca(OH)2 = CaCl2 + H2O and provide the correct coefficients for each compound. To balance HCl + Ca(OH)2 = CaCl... This video defines and compares the Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry acid and base theories. Then it provides examples for identifying the movement of protons (hydrogen ions) and conjugate acid and bas... About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... my name is jeff. Skip navigation A step-by-step explanation of how to draw the HCO3- Lewis Dot Structure (Hydrogen Carbonate or Bicarbonate Ion).For the HCO3- structure use the periodic tabl... In order to balance H2O2 = O2 + H2O you'll need to watch out for two things. First, be sure to count all of H and O atoms on each side of the chemical equat... http://leah4sci.com/acidbase presents: Acidity of Aromatic compounds - Video 8 in the Acid/Base sereisNeed help with orgo? Download my free guide '10 Secrets...
Copyright © 2024 top100.smartisbetter.site